In PHP, the ConfigProvider is a class that is part of an application’s bootstrap process. It’s a class or callable that returns configuration data telling the platform which middleware should run, in what order, and sometimes under what conditions.
If you’re talking specifically about the ConfigProvider in the Laminas/Mezzio ecosystem, it’s literally an array of configuration, settings, or anything else your application needs.
Where Is the ConfigProvider Used?
Mezzio (formerly Zend Expressive), Laminas, Slim, the Dotkernel Headless Platform, or other middleware-based frameworks often have a ConfigProvider class. In Laminas/Mezzio specifically, each module or package may contain a ConfigProvider that returns:
- Middleware pipeline configuration.
- Middleware classes or service names.
- Error-handling middleware, which should have the lowest priority.
- Middleware groups or nested arrays.
- Dependency injection mappings.
- Request Handlers.
Example in Dotkernel, which is an approach similar to Laminas/Mezzio:
class ConfigProvider
{
public function __invoke(): array
{
return [
'dependencies' => $this->getDependencies(),
'templates' => $this->getTemplates(),
];
}
public function getDependencies(): array
{
return [
'factories' => [
Handler\HomepageHandler::class => Handler\HomepageHandlerFactory::class,
Handler\SearchHandler::class => Handler\SearchHandlerFactory::class,
],
'invokables' => [
Console\GenerateSearchData::class => Console\GenerateSearchData::class,
],
];
}
public function getTemplates(): array
{
return [
'app' => [__DIR__ . '/../templates/app'],
'error' => [__DIR__ . '/../templates/error'],
];
}
}
What each item above means:
dependenciesis used by the dependency injector (like laminas-servicemanager) to construct every requested service.factorieswill have the factory build the service.invokableswill usenewdirectly.- You can also use
aliasesto redirect to another service name anddelegatorsto wrap the original service.
templatesdefines the paths for the template files.
How the ConfigProvider works
The ConfigProvider is automatically picked up by the framework during application bootstrap. Let’s look at it step by step:
- Merge the global configuration – All ConfigProviders are merged into one array.
- Read the configuration array – The call is similar to the below and expects an array of entries:
$config = $container->get('config')['key'] ?? [];
- Resolve item –
$app->pipe()is called to resolve one of the below instances:- Resolve the service name from the container
- Wrap the middleware, if an array is provided
- Call the closure or invokable object.
- Handle errors – This middleware is the last one in the pipeline to make sure it handles any exceptions.
- Execute at runtime – Laminas Stratigility iterates over the pipeline in the order it was registered.
- Each middleware can handle the request and return a response, or delegate execution to the next middleware in the pipeline, until a
ResponseInterfaceis returned to the client.
- Each middleware can handle the request and return a response, or delegate execution to the next middleware in the pipeline, until a
Below you can see how Mezzio and Dotkernel merge and use ConfigProviders to build the middleware pipeline and dependencies.
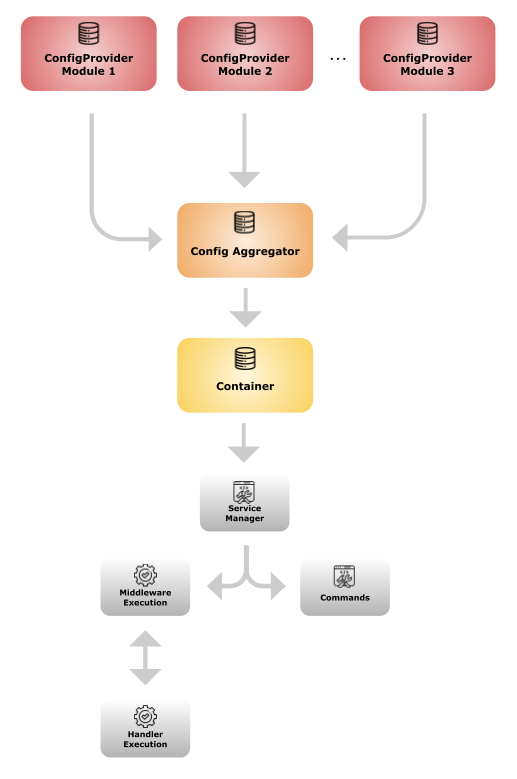
Benefits
- Centralized setup – Instead of hardcoding bootstrap code, you declare it in a config provider so it’s easy to read, change, or extend.
- Modular – Each package can ship with its own config without interfering with others.
- Container-friendly – It works well with frameworks using DI containers like Laminas ServiceManager, PHP-DI, or Pimple.
- Standardized service definitions – It has consistent rules for object creation that are separate from business logic.
- Auto-Discovery – In Laminas/Mezzio, the ConfigAggregator automatically loads and merges all ConfigProviders.
Dotkernel is an exception to this rule: new ConfigProviders have to be added manually in
config/config.php, because all the initial ConfigProviders required to install the applications are already injected.
- Environment-agnostic – It returns an array that defines dev, test, or prod environments.
- Testability – The consistent, central configuration promotes isolated (e.g. per-module) testing, easier swapping of dependencies and the assertion of pipeline setup (e.g. check if a config key is present).
Additional Resources
Looking for PHP, Laminas or Mezzio Support?
As part of the Laminas Commercial Vendor Program, Apidemia offers expert technical support and services for:
Leave a Reply